Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-10-27 Origin: Site





An ethernet switch is a key networking device that connects multiple wired devices within a local area network (LAN), enabling fast and efficient data exchange. Whether you’re setting up a home office, managing enterprise infrastructure, or integrating industrial systems, a cable ethernet switch ensures stable and high-speed connectivity. Understanding how an ethernet switch to router connection works can help you build a more reliable and scalable network for any environment.
An ethernet switch manages data traffic within a local area network (LAN). Unlike hubs, which broadcast data to all devices, a switch forwards data only to the intended recipient using MAC addresses. This selective forwarding improves network speed, conserves bandwidth, and enhances security.
When connecting a network device to a switch, the switch updates its MAC address table to remember which device is connected to which port. For example, when connecting a printer to a switch, data sent to the printer is routed directly to its port, minimizing unnecessary traffic.
Key roles of an Ethernet switch include:
Efficient packet forwarding within a LAN
Reducing collisions and network congestion
Supporting VLANs for network segmentation and enhanced security
Optimizing bandwidth usage across multiple devices
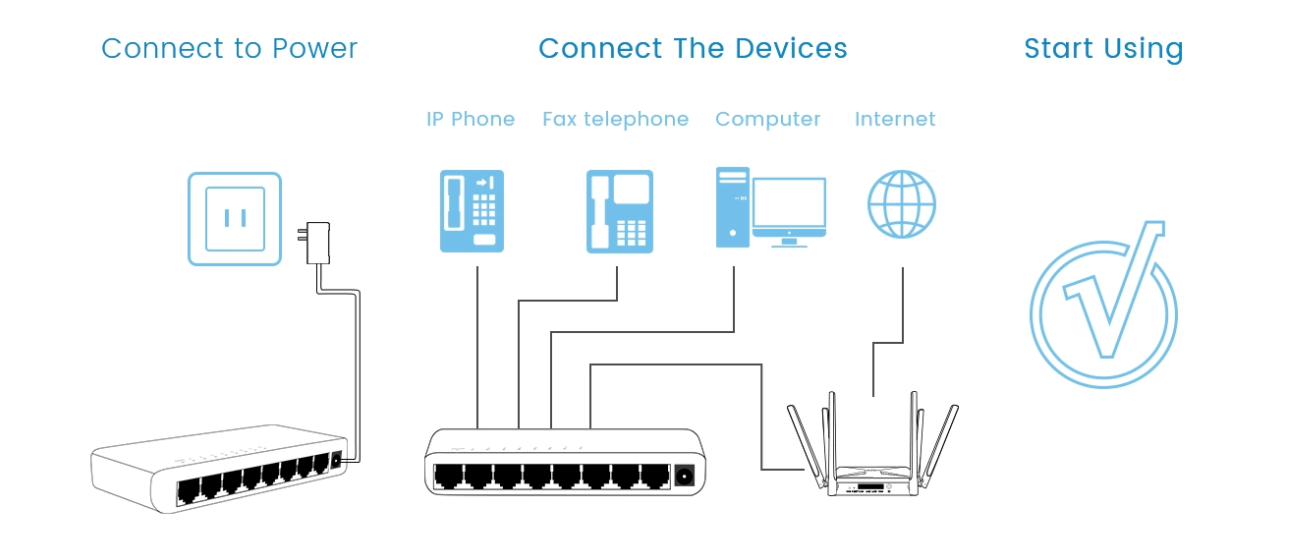
Using a cable ethernet switch is straightforward, yet the correct setup and understanding of its capabilities can greatly enhance network performance. Ethernet switches are versatile devices suitable for a variety of network setups, from small home offices to large enterprise networks. Here’s a detailed step-by-step guide on how they are typically used:
Connect the Power:
Start by plugging in the switch and connecting it to a stable power source. Some industrial or high-end switches also support Power over Ethernet (PoE), which can power devices like IP cameras or access points directly through the Ethernet cable, reducing the need for additional power adapters.
Connect Devices:
Use Ethernet cables to connect computers, printers, servers, IP phones, or other network-enabled devices to the switch ports. By doing so, each device becomes part of the same local area network (LAN), enabling seamless communication. In larger setups, using high-quality Ethernet cables ensures faster data transfer speeds and reliable connections.
Connect to Router:
To provide internet access to all devices in the network, connect one of the switch ports to a router using an Ethernet cable. This ethernet switch to router connection allows the switch to distribute network traffic efficiently while the router manages external network access. In enterprise environments, multiple switches may be connected to the same router to scale the network.
Configure the Switch (Optional):
While unmanaged switches are typically plug-and-play, managed switches provide additional configuration options. These include creating VLANs to segment network traffic, setting up Quality of Service (QoS) to prioritize critical applications like VoIP or video conferencing, and monitoring port activity for troubleshooting and security. Proper configuration helps optimize performance and enhances network control.
Test the Network:
After connecting devices and optionally configuring the switch, it’s important to test the network. Check that all connected devices can communicate with each other, access shared resources, and reach the internet if required. Many managed switches offer diagnostic tools to verify port status, monitor traffic, and detect potential issues, ensuring a stable and efficient network environment.
Expand and Scale the Network:
One of the key benefits of Ethernet switches is scalability. If more devices need to be added, additional switches can be connected via uplink ports, daisy-chaining or stacking switches to expand the network without sacrificing performance. Proper planning ensures that bandwidth and traffic management remain optimized even as the network grows.
By following these steps, a cable ethernet switch can efficiently distribute network traffic, enhance speed, and maintain reliable connections. Whether in a small office, a data center, or a manufacturing environment, understanding these usage steps helps ensure your network runs smoothly and securely.
Ethernet switches are highly versatile networking devices, playing a critical role in connecting multiple devices efficiently. Their applications span from small home networks to large-scale industrial systems, making them an essential component of modern LAN environments.
In home and small office setups, ethernet switches simplify network connectivity by allowing multiple devices—such as PCs, laptops, printers, smart TVs, and gaming consoles—to communicate seamlessly. Using a cable ethernet switch in these environments ensures faster and more stable connections compared to relying solely on Wi-Fi. This is particularly useful for bandwidth-intensive activities like HD video streaming, online gaming, or transferring large files between devices. For small offices, a switch provides a reliable way to share resources like networked printers and storage devices, improving overall productivity without complex network configurations.
In enterprise networks, ethernet switches are the backbone of internal communication, connecting hundreds or even thousands of devices across corporate offices, campuses, and data centers. Managed switches allow network administrators to create VLANs for segmenting traffic, implement Quality of Service (QoS) to prioritize critical applications, and monitor network performance for security and efficiency. These switches are crucial for environments that require high reliability, such as video conferencing systems, cloud-based applications, centralized file servers, and enterprise Wi-Fi access points. High-speed switches also help optimize bandwidth, reduce latency, and maintain seamless operation across multiple departments and floors.
Industrial ethernet switches are designed to withstand harsh conditions, making them suitable for factories, warehouses, transportation hubs, and other mission-critical environments. These rugged switches provide reliable connectivity for automated control systems, surveillance networks, and sensor-based monitoring systems, where downtime can result in significant operational disruptions. Industrial switches often support advanced features such as redundancy protocols, high-temperature operation, and vibration resistance to ensure continuous network availability even in extreme conditions.
A typical network setup often involves an ethernet switch to router connection, which enables all connected devices to access the internet through a single gateway. This setup allows for efficient distribution of network traffic while the router manages external communication. Switches can also be cascaded or stacked to expand network capacity, allowing organizations to scale their infrastructure as their networking needs grow. For example, multiple switches can interconnect in offices, data centers, or industrial facilities to create large, resilient networks that maintain high performance and minimal latency across all connected devices.

Ethernet switches offer numerous advantages that make them indispensable in both home and enterprise networks. Understanding these benefits helps network administrators and users optimize performance and maintain secure, scalable infrastructures.
One of the primary advantages of an ethernet switch is its ability to intelligently forward data packets only to the intended recipient. Unlike older networking devices such as hubs that broadcast data to all connected devices, switches use MAC addresses to determine the correct destination. This targeted approach significantly reduces unnecessary traffic, minimizes collisions, and improves overall network efficiency. By optimizing the flow of data, switches help ensure that high-bandwidth applications—like video conferencing, large file transfers, and cloud-based services—operate smoothly without interruptions.
Security is another key benefit of using ethernet switches. Managed switches provide advanced features such as VLANs (Virtual Local Area Networks), port-level controls, and MAC address filtering, which allow network administrators to segment traffic and limit access to sensitive information. By isolating different network segments, VLANs enhance data privacy and protect against unauthorized access or potential network attacks. This level of control is crucial for enterprise networks handling confidential business data or for industrial systems where secure communication between devices is critical.
Ethernet switches are highly scalable, allowing networks to grow as organizational needs evolve. Additional switches can be cascaded or stacked to expand network capacity without redesigning the entire infrastructure. This scalability ensures that networks can support more devices, higher bandwidth demands, and increasingly complex applications. Whether adding new workstations in an office, expanding a data center, or integrating IoT devices in an industrial environment, cable ethernet switches provide a flexible and cost-effective solution for network expansion.
Wired connections through a cable ethernet switch offer stable and high-speed performance that is difficult to achieve with wireless networks alone. This reliability is especially important for environments that require consistent connectivity, such as video streaming, VoIP communications, cloud computing, or real-time industrial monitoring. By providing dedicated bandwidth to each device, ethernet switches reduce latency and ensure that critical applications run smoothly. Whether in a home, office, or industrial setting, the dependable performance of ethernet switches supports uninterrupted network operations.
An ethernet switch is a network device that connects multiple wired devices within a local area network (LAN). It forwards data packets intelligently to the intended recipient using MAC addresses, improving network efficiency and reducing unnecessary traffic.
A cable ethernet switch receives data from connected devices, checks the destination MAC address, and forwards the data to the correct port. This ensures that only the intended device receives the information, optimizing bandwidth and enhancing network performance.
While an ethernet switch manages data traffic within a local network, a router connects different networks and manages external internet access. Typically, an ethernet switch to router connection is used to provide internet access to all devices in a LAN.
Yes, Ethernet switches can be connected to wireless access points. These access points then allow Wi-Fi devices to communicate with the wired network, combining wired and wireless connectivity.
Yes, ethernet switches improve network efficiency by directing data packets only to their intended devices, reducing collisions and congestion compared to hubs or shared networks.
In today’s connected world, an Ethernet switch is the key to creating a faster, more stable, and smarter wired network. Whether you’re upgrading your home setup or managing enterprise systems, choosing the right switch ensures seamless data flow, low latency, and long-term reliability.
At Shenzhen HS Fiber Communication Equipment CO., LTD., we specialize in high-performance Ethernet switches designed for modern networking demands. Explore our full range to power your connectivity with professional-grade stability and speed.